Lymph Node Exam
Lymphatic pathways are difficult to visualize in ordinary tissue and are better seen in an inflamed state (lymphangitis). Inflamed lymph nodes specifically are referred to as lymphadenitis.
Categories
Acute lymphadenitis
Rapid cellular infiltration stretches the capsule and causes pain/tenderness. Is associated with skin changes like erythema/drainage.
Chronic lymphadenitis
Slower, so less tenderness. Seen in rheumatoid arthritis, HIV, mononucleosis (Mono/EBV), or cancer.
Cancer and the Lymph System
Transport through the lymph system is the most common carcinoma pathway and follows drainage. Nodal enlargement could be from reactive hyperplasia or cancer spread.
Two thirds of NHL and almost all Hodgkin Lymphoma present with nontender nodal enlargement.
Examination
Normal nodes should be 1-2 cm, mobile, discrete, and nontender. Lymphadenopathy is when lymph nodes are enlarged. Hard, fixed nodes suggest malignancy.
Lymph nodes
- preauricular
- posterior auricular
- occipital
- tonsillar
- submandibular
- submental
- superficial cervical (anterior cervical)
- posterior cervical
- deep cervical chain
- supraclavicular
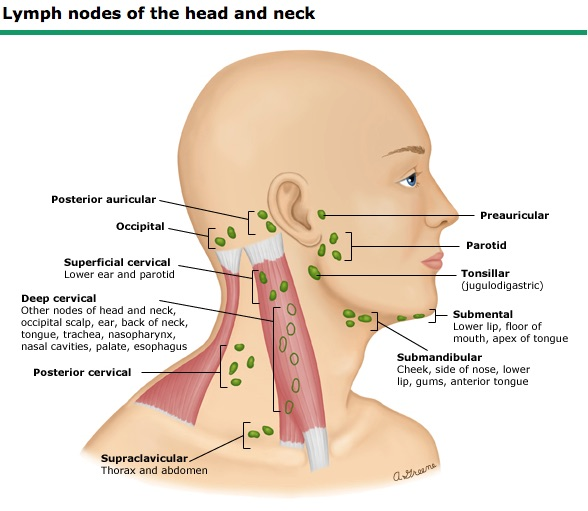
Supraclavicular nodes
Although these drain parts of the head and neck, the left supraclavicular lymph node can also drain parts of the thoracic area/GI. For more, see here: Circulatory System Primer > Lymphatic vessels.
Upper extremity nodes
The epitrochlear nodes drain the ulnar surface of the forearm as well as the 4th and 5th digits on the hand. Axillary lymph nodes drain the rest of the arm.
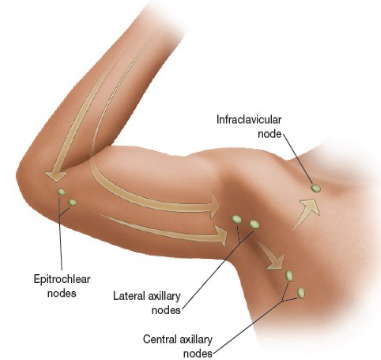
Chest wall and upper extremity nodes
These include the central axillary nodes, pectoral nodes, lateral nodes, and subscapular nodes.
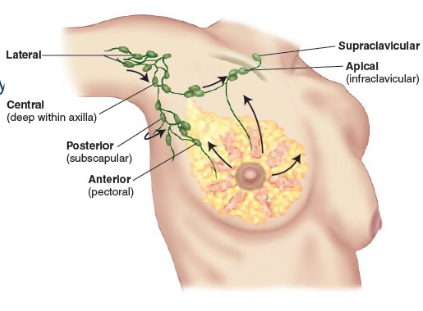
Clinical Pearl: Breast cancer
Generally in the upper/outer quadrant and will disseminate first to axillary lymph nodes.
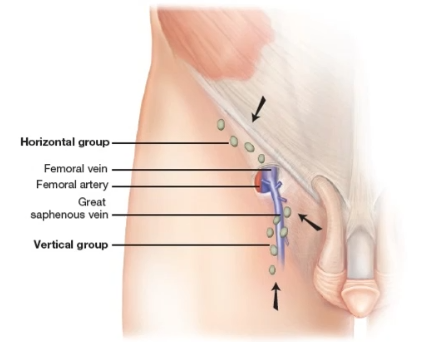
Lower extremity nodes
These include the horizontal group which drains the belt-to-bottom (lower abdomen, buttocks, anal canal, external genitalia, lower vagina), and the vertical group which drains the legs (great saphenous veins).
The lower calf drains into the small saphenous vein which is deep and not palpable.