Gastrulation And Embryonic Folding
Inductive interactions
How cells know where to go and what to differentiate into
Some ways cells can be inducted to differentiate or morph:
- Morphogens: dispersion of factors that influence the formation of cells into tissues. Concentration decreases farther away from the cell of origin which will affect cellular expression
- Extracellular matrix
- Direct cell contact
Gastrulation
The transformation of the bilaminar disk (epiblast + hypoblast) in 3 germ layers, later giving rise to the organ systems. All three germ layers come from the epiblast.
- Ectoderm: Form epidermis and neurons
- Mesoderm: Form muscles, vasculature, bones
- Endoderm: Form most GI structure, lungs, accessory organs
This process begins day 14 - 15, following Fertilization and Implantation with the formation of the primitive streak (PS). This starts at the caudal end and moves from a caudal to cranial direction, creating the cranial-caudal axis.
Formation of the germ layers
1. Endoderm
After PS formation, the epiblast cells ingress through the primitive groove and spread into the degenerating hypoblast cells. These cells transform from epithelial to mesenchymal cells. The first layer of cells ingress through the primitive groove and becomes the endoderm.
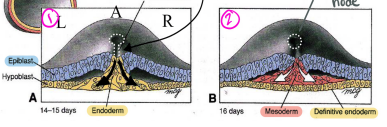
2a. Mesoderm and Ectoderm
The epiblast starts secreting hyaluronic acid & fibronectin which allows another layer to ingresses through the primitive groove between the two layers, settling superior to the endoderm. The middle layer then differentiates into the embryonic mesoderm. The remaining bottom layer of epiblast cells become the ectoderm.
The structure is now a trilaminar disk.
Clinical pearl: Kartagener's Syndrome
Cilia on the basal side of the ectoderm near the primitive node create currents that distribute important signaling molecules. Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) and Fibroblast Growth Factor 8 (FGF-8) are two such proteins that diffuse to the LEFT and activate a protein called Nodal.
In Kartagener's syndrome, abnormal dynein on the cilia disrupt the direction of diffusion, activating Nodal on the right. This can be lethal to the embryo and cause situs inversus (organs on the opposite side).
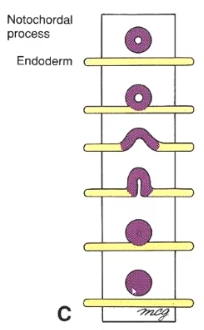
2b. Notochord
Cells that are ingressing through the primitive node migrate towards the Prechordal plate at the cranial end, forming a hollow structure called the notochordal process. The process will continue to move caudally and then fuses with the underlying endoderm which brings the Notochordal plate into contact with fluid within the yolk sac and signals the cells to reform into a solid mass called the Notochord.
Steps (note this occurs in the caudal direction):
- Migration through primitive node
- Notochordal process forms
- Fusion with endoderm
- Pops back up
- Notochord (no donut)
TL;DR The notochord is derived from the mesoderm.
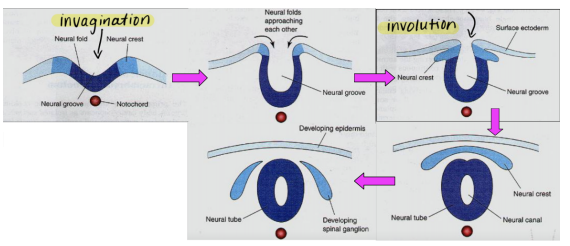
3. Neural tube transformation
The notochord releases growth factors which signal the ectoderm to proliferate. This thickening ectoderm is referred to as the neural plate which invaginates downward, creating the neural groove. Proliferation of cells along this groove causes the structure to involute, creating neural folds closer to each other. As the fold's edges fuse, the neural tube is formed.
The neural crest cells are hanging out somewhere between the tube and ectoderm.
Steps:
- Ectoderm proliferates, thickening
- Neural plate invaginates (neural groove)
- Neural groove involutes (neural folds)
- Neural folds fuse (neural tube)
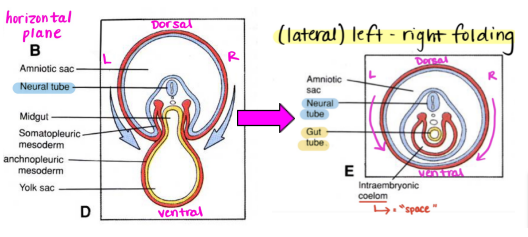
Embryonic folding
The trilaminar embryo undergoes convergent extension, forming a "tube within a tube".
The ectoderm is now on the exterior of the embryo (makes sense as it forms many superficial structures). We now have a dorsal and ventral axis.
Clinical Peals
Hydatidiform mole
Rare, cyst-like mass which can occur in 0.1 - 0.5% of pregnancies. Must be removed. This causes an excess of male genetic material with no fetus present.
Symptoms:
- High hCG
- Hypertension
- Edema
- Vagina bleeding
Prader-Willi Syndrome
Caused by deletion on chromosome 15Q11-13. Inherited from father.
Symptoms:
- Cognitive: CNS malformations, retardation
- Physical: Impaired body control, short stature, insatiable appetite
Angelman's Syndrome
Caused by deletion on chromosome 15Q11-13. Inherited from mother.
Symptoms:
- Cognitive: Happy demeanor, developmental delay, language difficulty
- Physical: Motor control and balance