Cholinergics
For more on the autonomic nervous system, see here: Autonomic Nervous System Effects Primer
Acetylcholine (Ach)
Created by combining Acetyl-CoA and choline via choline acetyltransferase (ChAT). It is released with a Ca2+ influx and binds to Nicotinic or Muscarinic receptors.
After binding, ACh leaves the receptor and is cleaved into choline and acetate via ACh Esterase (AChE). The choline is recycled back into the post-synaptic neuron.
Botulinum Toxin (Botox) disrupts vesicle fusion proteins at the NMJ, blocking release of ACh from the vesicle.
Structure
Ach has two charged centers which make it polar. This limits absorption across the GI tract and means it cannot be taken orally or cross cell membranes.
Receptors
Muscarinic
G protein coupled (GPCR) which are slower acting and take longer to reach the effect. They have structural differences and cannot currently be targeted individually.
M1 (q): Higher cognitive functions, enteric nervous system
M2 (i): Decreased heart rate and contractility of atria
M3 (q): Increased exocrine gland secretions, peristalsis, bladder contraction, bronchoconstriction, pupillary sphincter muscle contraction (miosis), ciliary muscle contraction (accommodation), insulin release, vasodilation
The q subunit receptors proceed down the IP3-DAG pathway while the i subunit receptor proceeds down the cAMP pathway.
Note: M3 does not act on smooth muscle receptors directly, as that would cause them to contract. Instead, they use downstream Nitric Oxide (NO) which diffuses to the smooth muscle and increases cGMP, causing relaxation.
See here for a primer on signaling subunits s, i, and q: Signal Transduction Primer > Guanine binding proteins
Nicotinic
These are ligand-gated ion channels which cause depolarization at the target.
Neuronal receptors are located on the ganglia, adrenal medulla, and CNS.
Muscular receptors are located at the neuromuscular junction on muscle cells.
Parasympathetic
Eyes
Pupils constrict, improving near vision.
Glands
Increase in secretions (lacrimal, nasal, and salivary).
Bronchi
Increase in secretions and constriction of smooth muscle.
Heart
Vagal nerve tone results decreased heart rate (via sinoatrial node). Conduction through the AV node decreases and atrial contractility lowers.
Gastrointestinal/Urinary
Promotion of digestion and urination. Increased gastric acid secretion in the stomach, motility of smooth muscles, and relaxation of sphincters. Contraction of bladder.
Sympathetic
Eyes
Pupils dilate, allowing in more diffuse light.
Bronchi
Dilation and relaxation of smooth muscle.
Heart
Increase in heart rate (via sinoatrial node). Conduction through AV node increases and contractility for atria and ventricles increases.
Release of epinephrine (from adrenal medulla) leads to dilation of blood vessels and increases liver blood volume.
Gastrointestinal/Urinary
Downregulation of digestion and urination. Decreased gastric acid secretion in the stomach, lowered motility of smooth muscles, and constriction of sphincters. Contraction of bladder.
Kidney
Increased renin → increased sodium retention → increased water retention
Increased glycogen breakdown, glucose release
Skin
Piloerection and sweating.
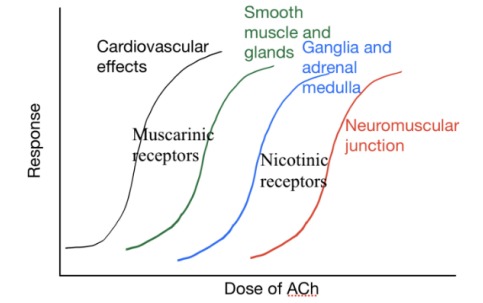
Dose-Response
The autonomic effects will not be seen at the same dosage of cholinergic drugs. This is the reason Ach cannot be injected to solve NMJ disorders (i.e., Myasthenia Gravis), as the high required dosage will have side effects.