Synaptic Cell Biology
Chemical Synapse
Presynaptic neuron sends signal to a postsynaptic neuron via neurotransmitters. The synapse refers to the space between cells (20-40 nm).
Post-synaptic receptors
- Ionotropic: Ligand-gated ion channels. Quickly alter membrane potential.
- Metabotropic: G-protein coupled. Result in signal cascade which have slow, but long lasting inner-cell effects.
Neurotransmitter release
Neurotransmitters are released via exocytosis. This process is calcium dependent and occurs when an action potential opens a voltage-gated calcium channel (VGCC). The concentration of calcium is much higher outside the cell.
Vesicles fuse with the cell membrane using SNARE proteins, specifically synaptotagmin which is a Ca2+ sensor. Tetanus and botulinum toxin (Botox) inhibit SNARE function.
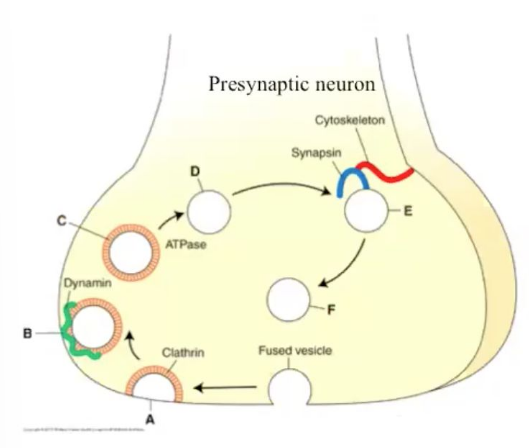
Vesicles are recycled via endocytosis. This process is clatherin-dependent. Dynamin will pop the clatherin-coated vesicle off the side of the cleft for re-use.
Key Neurotransmitter Metabolism
| Production | Production Enzymes | Release | Recycling/Degradation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetylcholine (ACh) | 1. Acetyl CoA + Choline → ACh | 1. Choline AcetylTransferase (ChAT) | ACh vesicle transporter (Ca2+ mediated) | Acetylcholine Esterase (AchE) |
| Norepinephrine (NE) | 1. Tyrosine → 2. L-DOPA → 3. dopamine → NE (inside presynaptic vesicle) | 1. Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH), 2. DOPA Decarboxylase, 3. DA Beta Hydroxylase (DBH) | Monoamine vesicle transporter (VMAT) (Ca2+ mediated) | Monoamine oxidase (MAO), catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) |
| Epinephrine (E) | 1. NE → E (NE leaked out of vesicle, converted in cytoplasm) | 1. phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase (PNMT) | Monoamine vesicle transporter (VMAT) (Ca2+ mediated) | Monoamine oxidase (MAO), catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) |
| Serotonin (5-HT) | 1. Tryptophan → 2. 5-HTP → 5-HT | 1. Tryptophan-5-hydroxylase, 2. Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase (AADC) | Monoamine vesicle transporter (VMAT) (Ca2+ mediated) | Monoamine oxidase (MAO) |
| Note: Noradrenaline and Adrenaline are alternative names for Norepinephrine and Epinephrine, respectively. | ||||
| Note: Serotonin will bind to both CNS and PNS targets. PNS targets can include bone remodeling, lipolysis, glucose metabolism, bone marrow, and the gut microbiome. |