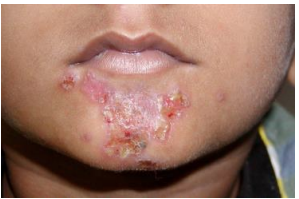
Dermatology Exam
An extensive history is important for this exam.
First, identify the primary lesion, noting what we can see. Next, look at the distribution or which part of the skin is primarily affected (e.g. epidermal changes, vascular, dermal process, subcutaneous mass).
Primary: Macule, papule, nodule, vesicle, pustule, wheal
Secondary (changes with the primary): Scale, crust, excoriation, ulcer, atrophy, scar
Flat: Macule, telangiectasia, purpura
Elevated: Papule, plaque, nodule, wheal
Depressed: Atrophy, erosion, ulcer, scar
Macula have a diameter < 1 cm while patches have a diameter > 1 cm. If it is raised, it is not a macule or a patch. Papule are raised lesions < 1 cm while plaques are flat-topped lesions > 1 cm.
Lichenification
The epidermis thickens and causes accentuation of natural skin lines. Caused by prolonged scratching or rubbing of the skin. Can be covered by scales which can be made transparent with alcohol.
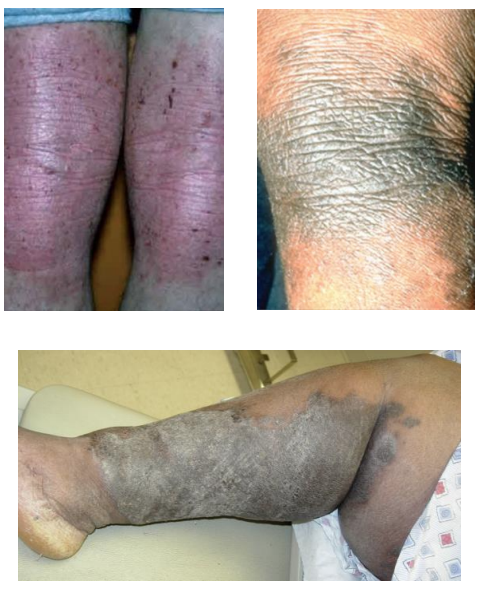
Lumps and Bumps
Nodules have a diameter > 1 cm. Palpable, solid and dome shaped. Usually found in the dermal of subcutaneous tissue.
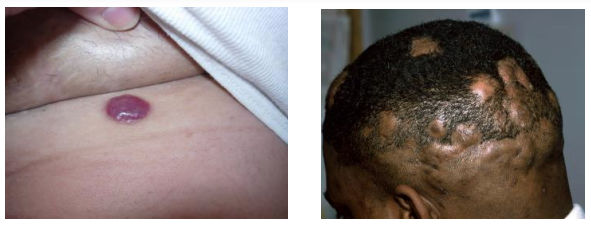
Tumors have a diameter > 2 cm and are also solid growths.
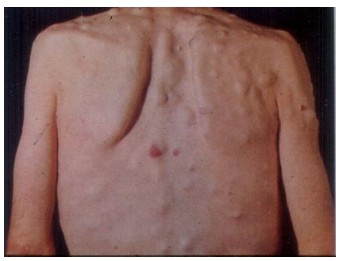
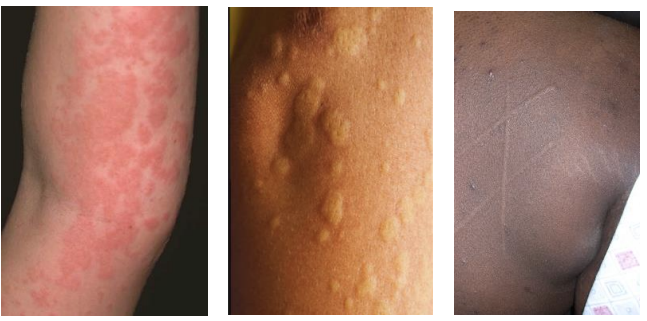
Urticaria
Hive or wheal. A special type of raised lesion which is a transient (< 24 hours), edematous papule or plaque caused by edema of the dermis. Dermographism is "skin writing" which causes the raised areas with gentle pressure or scratching.
Blisters
Vesicle
Small blisters (< 1 cm) filled with fluid (clear, serous, or hemorrhagic).
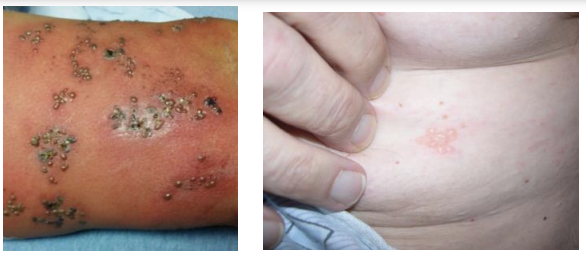
Bulla
Large blisters (> 1 cm) filled with fluid (clear, serous, or hemorrhagic).
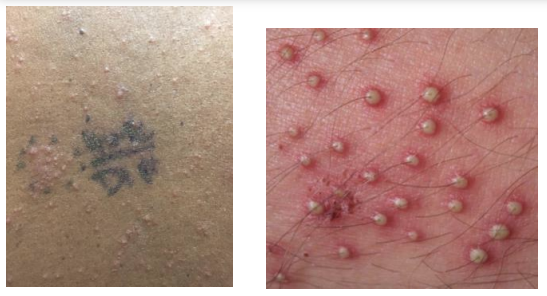
Pustule
Small elevation of the skin containing pus. Follicular or non-follicular.
Atrophy
Epidermal atrophy: Thinning of the epidermis, leading to wrinkles
Dermal atrophy: Loss of dermal collagen and/or elastin, leading to a depression
Can be distinguished from lichenification as the skin will not be thickened.
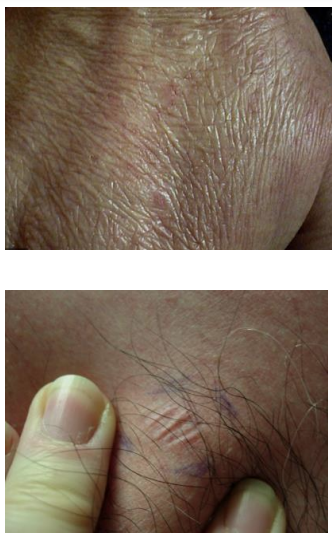
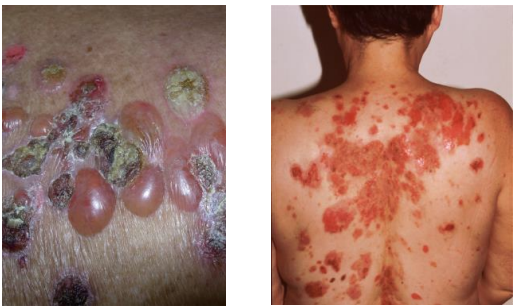
Erosion
Partial loss of the epidermis (epithelium). Can occur after a vesicle or bulla forms and the top feels off, or because of scratching.
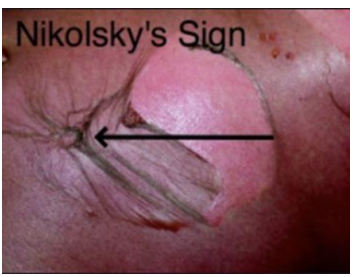
Nikolsky sign: Lateral pressure results in shearing
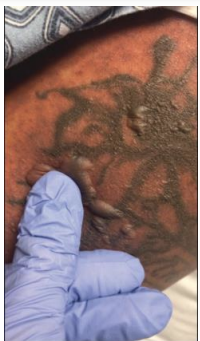
Asboe-Hansen sign: Intact blister spreads with pressure
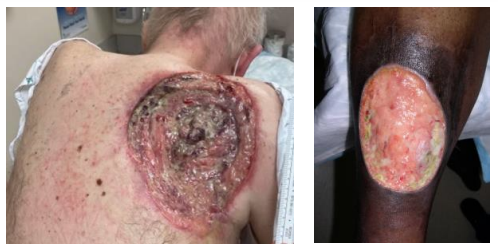
Ulcer
Full thickness loss of the epidermis and potential loss of dermis/subcutis.
Cicatrix (scar)
Tissue which forms in a wound during healing.
Atrophic scars: Depressed
Hypertrophic scars: Raised
Keloid scars: Extend beyond the boundaries of the original injury
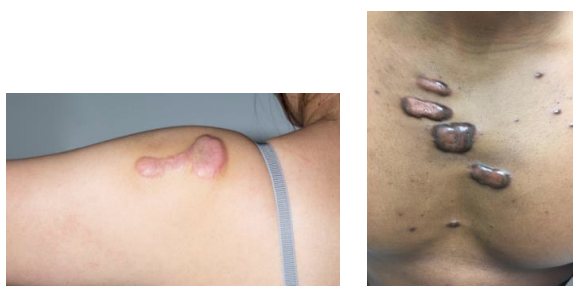
Scale
Accumulation of stratum corneum from increased proliferation or delayed desquamation. White or yellow, rough.
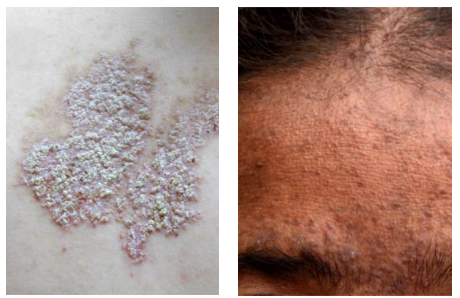
Crust
Dried sebum, pus, or blood mixed with epithelial or bacterial debris. Indicates infection or blistering.