Integument
A protective outer layer.
Epidermis: Outermost later
Dermis: Thicker, inside later
Hypodermis: Superficial fascia laying underneath the dermis. Not actually part of the integument.
Epidermis
It's your outer meat flesh. You know what this does.
Thin epidermis: Covers most of the body. Has a thin corneum layer without a lucidum.
Thick epidermis: Present in parts of body vulnerable to abrasion. Has a thick corneum and a lucidum.
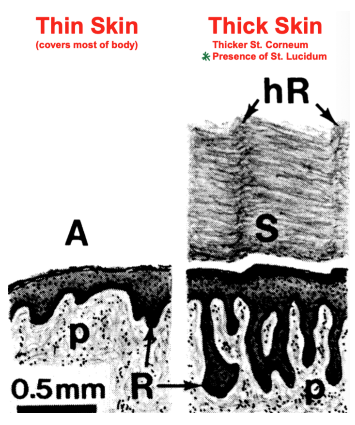
Layers
Courtney Love Gets Syphilis Biweekly
Corneum, Lucidum, Granulosum, Spinosum, Basale
Stratum Corneum
Contains non-living cells, makes the fingerprint
Stratum Lucidum
Contains non-living cells, only in thick epidermis
Stratum Granulosum
Keratohyalin granules: Bund filaggrin to keratin
Lamellar granules: Membrane coated, secrete lipid sheets to form intercellular cement (protect skin from desiccation)
Stratum Spinosum
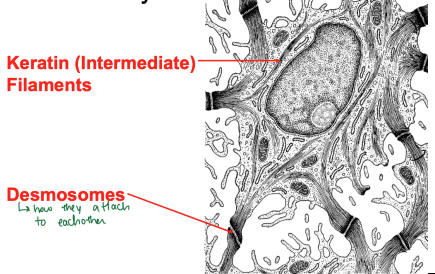
Keratinocytes connect to each other using cadherin proteins. Desmosomes give a "spiny" appearance as an artifact of tissue shrinkage.
Stratum Basale
Attached to basement membrane via hemidesmosome connections via integrin proteins.
Cell types
Keratinocytes
Filled with keratin (intermediate) filaments, attached via desmosomes.
Langerhan's cells
Phagocytic cells derived from monocytes with immune functions.
Merkel's cells
Perform sensory functions and contain neurotransmitter filled granules. Located in basale.
Melanocytes
Produce melanin via tyrosinase. Melanin granules travel to keratinocytes in spinosum and are arranged to be adjacent to the nucleus to protect DNA from sun damage. Found in basale.
Dermis
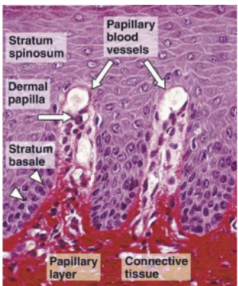
Papillary layer
Contacts the epidermis (basale) where it forms peg and socket connections, preventing it from shearing off. Contains capillaries and Meissner's corpuscles (mechanoreceptors).
Reticular layer
Dense connective tissue responsible for wrinkles. Contains fibroblasts, type I collagen, and elastic fibers. Also contains Pacinian corpuscle for deep touch/pressure sensitivity.
Also contains arteriovenous (AV) shunts responsible for thermal regulation. Will vasoconstrict in the cold and vasodilate in the heat.
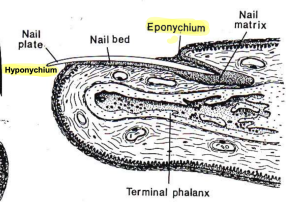
Nails
Eponychium: Cuticle/nail bed which the nail emerges from
Hyponychium: Skin underneath nail plate
Hair follicles
Shaft
The hair shaft is surrounded by the internal root sheath which stops at the sebaceous gland. The external root sheath extends into the epidermis and connects to an erector pili muscle, straightening the hairs when stimulated.
Root
Contains the hair follicle as well as the bulb which houses the germinal matrix responsible for hair cell division. Also found here are melanocytes and papillary layer of dermis.
Glands
For classification, see here: Histological Techniques, Epithelium, and Glands > Classification
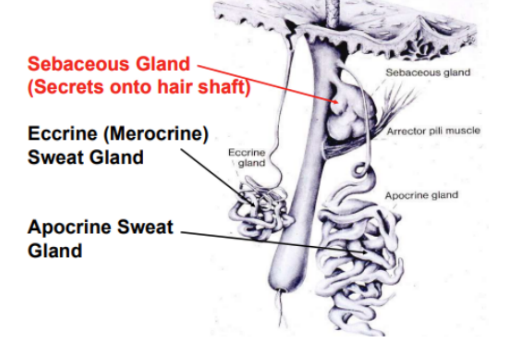
Sebaceous
Secretes onto hair shaft, simple branched acinar (holocrine secretion)
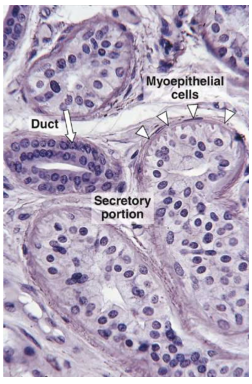
Eccrine
Sweat gland, secretes to skin. Are Simple, coiled, and unbranched (merocrine secretion). Has a secretory duct in the dermis containing sweat as well as secretory granules/pheromones. Also secretes protein free filtrate. The excretory duct is stratified cuboidal epithelium and will grab Na and Cl salts before they're released.
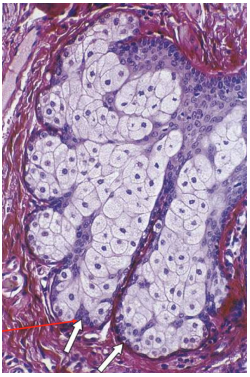
Apocrine
Sweat gland, secretes onto hair shaft. Simple, coiled, tubular. Note the secretion is MEROCRINE despite the name.